| |
| |
| Social Engineering - The Human Factor |
| Author:
Dinesh Shetty |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
|
Cyber security is an increasingly serious issue for the complete
world with intruders attacking large corporate organizations with
the motive of getting access to restricted content.
CSI Computer
Crime and Security Survey report for the year 2010-2011 stated that
almost half of the respondents had experienced a security incident,
with 45.6% of them reporting that they had been subject of at least
one targeted attack.
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Merely trying to prevent infiltration on a technical level and
ignoring the physical-social level, cent percent security can never
be achieved. Couple of examples can be the scenes from Hackers which
shows Dumpster diving in the target company's trash in order to
obtain financial data from printouts and the scene from War Games
where Matthew Broderick's character studied his target before
attempting to crack the password of the military computer system.
'Social Engineering' is a threat that is overlooked in most of the
organizations but can easily be exploited as it takes advantage of
human psychology rather than the technical barricades that surrounds
the complete system. Below is a classic example of this:
A
person receives an e-mail on his official mailbox saying that his
computer has been infected with a virus. The message provides a link
and suggests that he downloads and installs the tool from the link
to eliminate the virus from his computer. The person in a state of
confusion clicks on the link to remove the virus from his computer
but unwittingly giving a hacker an easy entrance into his corporate
network.
To ensure complete security of an organization from all
kinds of internal and external factors, the security consultant must
have complete knowledge of the Social Engineering cycle, the
techniques that can be used by an attacker and the counter-measures
to reduce the likelihood of success of the attack.
In this
paper we are going to take you through the various phases so as to
understand what is Social Engineering, Social Engineering Lifecycle,
the various Techniques used in Social Engineering attack with
detailed examples and then finally conclude with the
counter-measures to protect against each of the Social Engineering
attack techniques. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The term "Social Engineering" can be
defined in various ways, relating to both physical and cyber aspects of
that activity. Wikipedia defines social engineering as:
"...the
art of manipulating people into performing actions or divulging
confidential information".
Other authors have provided the
following definitions:
"An outside hacker's use of psychological
tricks on legitimate users of a computer system, in order to obtain
information he needs to gain access to the system".
"The practice
of deceiving someone, either in person, over the phone, or using a
computer, with the express intent of breaching some level of security
either personal or professional".
"Social Engineering is a
non-technical kind of intrusion relying heavily on human interaction
which often involves tricking other people into breaking normal security
procedures" the attacker uses social skills and human interaction to
obtain information about an organization or their computer systems.
In reality Social Engineering can be any of these definitions
depending on the circumstances that surround the attack. Social
Engineering is actually a hacker?s manipulation of the natural human
tendency to trust so as to get sensitive information needed to gain
access to a system. Social Engineering does not require high level of
technical expertise but requires the individual to have decent social
skills.
Many people, for several decades have used social engineering
as a method to research and collect data. These early social engineers
would use the gathered information as a form of blackmail against the
other organizations. Social engineering has been used to gain
unauthorized access into several huge organizations. A hacker who spends
several hours trying to break passwords could save a great deal of time
by calling up an employee of the organization, posing as a helpdesk or
IT employee, and can just asking for it. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Every Social Engineering attack is
unique, but with a little understanding of the situations encountered,
we can draft a rough cycle of all the activities that a Social
Engineering project goes through leading to a successful outcome.
The below figure shows a general representation of the Social
Engineering Life Cycle in four main stages: |
| |
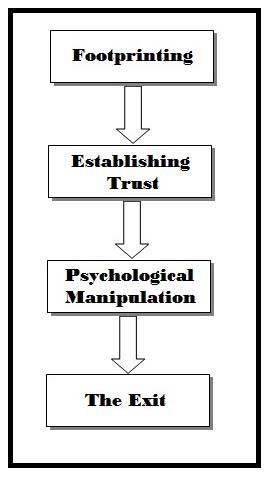 |
| |
| |
|
It is the technique of accumulating
information regarding the target(s) and the surrounding environment.
Footprinting can reveal the individuals related to the target with whom
the attacker has to establish a relationship, so as to improve the
chances of a successful attack.
The information gathering during
the Footprinting phase includes but is not limited to:
|
- List of employee names and phone numbers
- Organization Chart
- Department Information
- Location
information
|
Footprinting generally refers to one of the pre-attack phases;
tasks performed prior to doing the actual Social Engineering attack.
Some of the tools like Creepy,
SET and
Maltego make Social Engineering
engagements easier.
|
| |
| |
|
Once the possible targets have been listed
out, the attacker then moves on to develop a relationship with the
target who is usually an employee or someone working in the business so
as to develop a good rapport with them.
The trust that the social
engineer is gaining will later be used to unveil confidential pieces of
information that could cause severe harm to the business. |
| |
| |
|
In this step, the social engineer manipulates
the trust that he has gained in the previous phase so as to extract as
much confidential information or get sensitive operations related to the
target system performed by the employee himself so as to penetrate into
the system with much ease.
Once all the required sensitive
information has been collected, the social engineer may move on to the
next target or move towards exploiting the actual system under
consideration. |
|
| |
|
Now, after all the actual information has been
extracted, the Social Engineer has to make a clear exit in such a way so
as not to divert any kind of unnecessary suspicion to himself.
He
makes sure to not leave any kind of proof of his visit that could lead a
trace-back to his real identity nor link him to the unauthorized entry
into the target system in the future.
|
| |
|
|
| |
| |
| Every Social Engineer targets specific
behavioral traits in the victim so as to extract maximum information out
of him. These behavioral traits include but are not limited to: |
- Excitement of Victory
Mr. X gets an e-mail
stating, "You have won 1 Million Dollars and to claim the winning
amount, fill in the attached document and forward it to the email
id: XXXX@XXXX.com. Switch off your antivirus as it may block the
download due to highly encrypted Digital Signature of the
documents". Out of Excitement he switches off his Antivirus and
proceeds as ordered and downloads the document and opens it but
finds it corrupted. Little does he know that he has just downloaded
a malware on his machine which allows the email sender to gain
remote access to his machine.
- Fear of Authority
Many people are
apprehensive in the presence of someone they perceive as an
authority figure, it is not that person they are apprehensive about
but most likely the position and power of the person that
intimidates them and makes them.
The attackers take on roles of
authority figures such as law enforcement officers or high-ranking
company officials to extract sensitive organizational information
from the victims.
- Desire to be helpful
Keith A. Rhodes,
chief technologist at the U.S. General Accounting Office, which has
a Congressional mandate to test the network security at 24 different
government agencies and departments said in one of his interviews
that, "Companies train their people to be helpful, but they rarely
train them to be part of the security process. We use the social
connection between people, their desire to be helpful."
People in
their desire to be helpful and to solve other peoples queries, give
out a lot of information that otherwise should not be disclosed to
an outsider as it could give an attacker a chance to get
unauthorized access to the target system causing a possible loss.
- Fear of Loss
Mr. X gets an e-mail
stating, "You have won 1 Million Dollars and to claim the winning
amount, deposit $75,000 in Account number: XXXXXX in 10 days from
receiving this e-mail, failing to which the winning amount would be
declared unclaimed and there would be a nee lucky-draw to decide the
next winner". Out of fear that he might lose such a good
opportunity, he deposits the amount to the account number provided.
When his future replies to the e-mail address goes unanswered for
the next two months nor does the 1 Million Dollar gets deposited to
his account, he understands that he has been scammed.
- Laziness
All of us have come across
some or the other job that requires us to do only a specified set of
activities and not linger around looking for better ways of doing
that activity. This causes boredom to the person who performs the
same task repeatedly on daily basis and over the time learns
"shortcuts" to do the tasks using minimal efforts and still meeting
the targets. Such individuals over a period of time become lazy and
are susceptible to attackers who target such individuals as they
know that they would get the required information with much ease due
to the laid back attitude of these individuals towards their work.
- Ego
Many a times, the attacker makes
the person more emotionally sure of himself/herself and thus
removing the logical awareness of the security breach that is
occurring.
The result is that, the person being hacked senses no
harm in providing whatever it is that the attacker is requesting.
The reason that such an attack succeeds is that the attacker is a
receptive audience for victims to display how much knowledge they
have.
- Insufficient knowledge
Knowledge about
the target system is one of the key factors that differentiate the
attacker from other employees of the organization. Many a times, due
to lack of proper training, the employees are themselves not sure if
they have complete knowledge about the product and Social Engineers
take advantage of such situations by creating a sense of urgency and
not allowing the employee much time to think and understanding the
fact that they are under attack.
|
|
|
|
|
| |
The old-fashioned technical way of breaking
into the computer systems by brute-forcing the user logins or ports have
now been replaced by sophisticated methods that not only are easier, but
yield better and faster results based on human psychology. These attacks
can help the attacker get access to any system irrespective of the
platform, software or hardware involved.
How exactly goes a
person to carry out Social Engineering attack? The figure below shows
some of the most popular techniques used to perform a Social Engineering
attack: |
| |
 |
| |
- Shoulder Surfing
Shoulder surfing is a
security attack where-in, the attacker uses observational
techniques, such as looking over someone's shoulder, to get
information while they are performing some action that involves
explicit usage of sensitive, visible information. This can be
performed at a close range as well as at a long range using
binoculars or other vision-enhancing devices.
- Dumpster Diving
Many a times, huge
organizations dump items like company phone books, system manuals,
organizational charts, company policy manuals, calendars of
meetings, events and vacations, printouts of sensitive data or login
names and passwords, printouts of source code, disks and tapes,
company letterhead and memo forms, and outdated hardware carelessly
into the company dumpsters. The attacker can use these items to get
a huge amount of information about the company organization and
network structure.
This method of searching through the dumpster, looking for
potentially useful information discarded by a company?s employees is
known as Dumpster Diving.
- Role playing
It is one of the key
weapons for a Social Engineer. It involves persuading or gathering
information through the use of an online chat session, emails, phone
or any other method that your company uses to interact online with
the public, pretending to be a helpdesk, employee, technician,
helpless or an important user to divulge in confidential
information.
- Trojan horses
It is one of the most
predominant methods currently used by hackers that involve tricking
the victims to download a malicious file to the system, which on
execution creates a backdoor in the machine that can be used by the
attacker any time in the future and thus having complete access of
the victim?s machine.
- Phishing
It is the act of creating and
using Websites and e-mails designed to look like those of well-known
legitimate businesses, financial institutions and government
agencies to deceive Internet users into disclosing their personal
information and falsely claiming to be an established legitimate
enterprise in an attempt to scam the user into surrendering private
information that will be used for identity theft.
- Surfing Organization Websites & Online forums
Huge amount of information regarding the organization
structure, email ids, phone numbers are available openly on the
company website and other forums. This information can be used by
the attacker to refine his approach and create a plan on whom to
target and the method to be used.
- Reverse Social Engineering
A reverse
social engineering attack is an attack in which an attacker
convinces the target that he has a problem or might have a certain
problem in the future and that the attacker, is ready to help solve
the problem. Reverse social engineering involves three parts:
-
Sabotage: After the attacker gains a simple access to the system, he corrupts the system or gives it an appearance of being corrupted. When the user sees the system in the corrupted state, he starts looking for help so as to solve the problem.
-
Marketing: In order to make sure that the user approaches the attacker with the problem, the attacker advertises himself as the only person who can solve the problem.
-
Support: In this step, he gains the trust of the target and obtains access to sensitive information.
|
| |
| |
| |
There is no effective way to protect against a
Social Engineering attack because no matter what controls are
implemented, there is always that human factor which influences the
behavior of an individual.
But, there are certain ways to reduce the
likelihood of success of the attack. It is also important for
organizations to establish a clear and strong security policy and
processes to reduce the threat of social engineering.
The
following are some of the steps to ensure protection against Social
Engineering attack: |
- Security Awareness Trainings
Security
Awareness is the simplest solution to prevent Social Engineering
attacks. Every person in the organization must be given basic
security awareness training on timely basis that he/she should never
give out any information without the appropriate authorization and
that he/she should report any suspicious behavior.
- Background Verification
There is many
a chance that attacker may join the company as an employee so as to
gather insider information about the company. This makes background
screening a really important part of company policies to counter
Social Engineering attack. It should not only be limited to internal
employees but must also be extended to vendors and other contractual
workers too before they become the part of the organization or are
given access to the organization network.
- Physical security
There should be proper
access control mechanism in place to make sure that only authorized
people are allowed access to restricted sections of the
organization. There should be no tail-tagging.
- Limited data leakage
There should be
constant monitoring as to what all information about the
organization is floating on the World Wide Web. Any kind of
irregularity should be immediately taken care of. This will make
passive information gathering difficult for the attacker.
- Mock Social Engineering drills
Special
Social Engineering activities should be performed on the internal
employees of the organization by either the security team or by the
vendor so as to keep track of the security awareness levels in the
organization.
- Data Classification policy
There
should be proper classification of data on the basis of their
criticality levels and the access personnel. Data classification
assigns a level of sensitivity to company information. Each level of
data classification includes different rules for viewing, editing
and sharing of the data. It helps to deter social engineering by
providing employees a mechanism for understanding what information
can be disclosed and what cannot be shared without proper
authorization.
|
| |
| Some of the other controls that should be taken
care of, to reduce the success of a Social Engineering attack are listed
below: |
- Install and maintain firewalls, anti-virus, anti-spyware
software's, and email filters.
- Never allow people to tailgate with you.
- There should be a proper Incident response strategy set
for the organization.
- Usage of corporate ID's on public domain, blogs,
discussion forums etc should be restricted.
- Pay attention to the URL of a web site. Though malicious
web sites generally look identical to a legitimate site, but the URL
may use a variation in spelling or a different domain.
- Confidential and critical online details like corporate
mail box should not be accessed in public places, cafes, and hotels
etc. where Internet security cannot be trusted.
- Don't send sensitive information over the Internet before
checking a web sites security.
- Don't reveal personal or financial information in email,
and do not respond to email solicitations requesting this
information.
- Ensure all physical entry and exit points are secured at
all times.
- Do not provide personal information or information about
your organization to anyone unless you are certain of the person's
authority to have that information.
- Use virtual keyboard where applicable.
- Be very careful what is provided on your company web site.
Avoid posting organizational charts or lists of key people wherever
possible.
- Make sure to shred any document that is discarded that may
contain sensitive data.
|
| |
|
|
Through this article we can understand that, however secure your
application is, it is always vulnerable to one thing "The Human Factor".
This human factor is the weakest link in security which can be patched
not by one time training but only by an ongoing process of improvement.
Many times it's rather the interaction between the data and the
person has to be secured rather than the interaction between data and
server. |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |